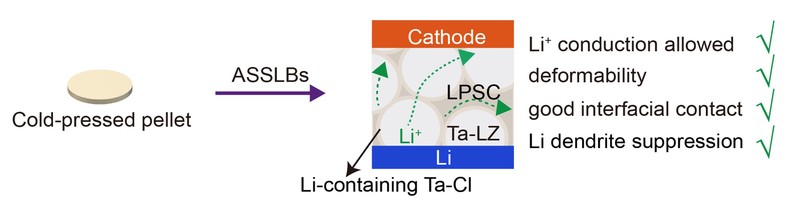
Garnet Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO)-based solid-state electrolytes (SSEs) hold promise for realizing next-generation lithium metal batteries with high energy density. However, the high stiffness of high-temperature sintered LLZO makes it brittle and susceptible to strain during the fabrication of solid-state batteries. Cold-pressed LLZO exhibits improved ductility but suffers from insufficient Li+ conductivity. Here, we report cold-pressed Ta-doped LLZO (Ta-LZ) particles integrated with ductile Li6PS5Cl (LPSC) via a Li+ conductive Li-containing Ta-Cl structure. This configuration creates a continuous Li+ conduction network by enhancing the Li+ exchange at the Ta-LZ/LPSC interface. The resulting Ta-LZ/LPSC SSE exhibits Li+ conductivity of 4.42 × 10–4 S cm–1 and a low activation energy of 0.31 eV. Li symmetric cells with Ta-LZ/LPSC SSE demonstrate excellent Li dendrite suppression ability, with an improved critical current density of 5.0 mA cm−2 and a prolonged cycle life exceeding 600 h at 1 mA cm-2. Our finding provides valuable insights into developing cold-pressed ceramic powder electrolytes for high-performance all-solid-state batteries.