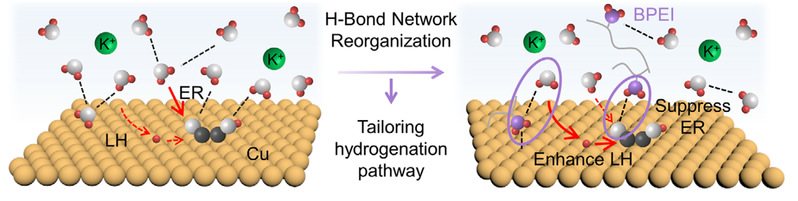
interfacial hydrogen-bond networks without altering catalyst electronic properties.In situ Raman spectroscopy captures enhanced *OCHCH2/*OCHCH3 intermediates, directly correlating ethanol selectivity with suppressed ER pathway. Combined experimental and theoreti calstudies establish quantitative relationships between hydrogen-bond strength and pathway selectivity. This strategy achieves 38.7% ethanol Faradaic efficiency (FE) at 900 mA cm−2 on CuO-derived catalysts (116% improvement) and 53% at 800 mA cm−2 on CuAg systems—among the highest reported efficiencies. Our findings reveal that controlling competitive hydrogenation pathways through interfacial engineering provides an independent parameter for steering CO2 reduction selectivity.
论文链接
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202523475